
The example will stat the html directory seen above.
This method is generally used against a single file, while the ls command is used against a list of files. the wordpress directory was assigned inode 405570Īnother method of viewing a file’s inode is to use the stat command.For more details about this command, refer truncate man pages. the html directory was assigned inode 276944 The above command will create a file called ostechnix.txt with size exactly 5MB.The first column of the returned listing is the assigned inode. In the example above two directories are returned by the ls command. When used with the -i flag the results for each file contains the file’s inode number. The simplist method of viewing the assigned inode of files on a Linux filesystem is to use the ls command. The ls command is useful for discovering the inode number for a list of files in a directory, while the state command is better suited for single files or directories. There are two commands that can be used to view a file or directory’s inode, and they are ls and stat.
File details linux how to#
In this tutorial, you are going to learn how to view the inode number assigned to a file or directory. These unique IDs are used by the filesystem’s database in order to keep track of files. The Vim text editor is successfully installed.Files written to Linux filesystems are assigned an inode. Processing triggers for man-db (2.8.7-3). Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/ex (ex) in auto m Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/view (view) in au Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/vi (vi) in auto m Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/rview (rview) in Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/rvim (rvim) in au Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/vimdiff (vimdiff) Update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/vim.basic to provide /usr/bin/vim (vim) in auto Selecting previously unselected package vim.
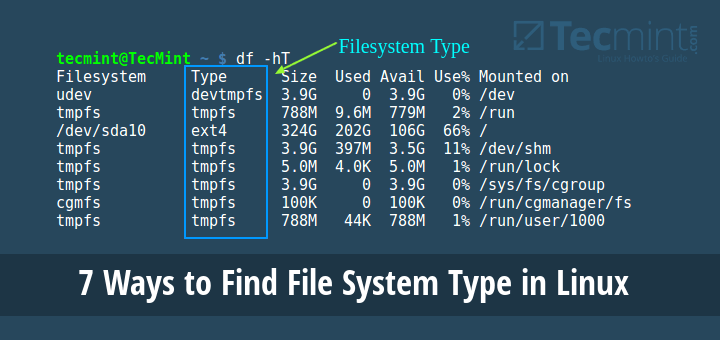
Īdding 'diversion of /usr/share/vim/vim81/doc/help.txt to /usr/share/vim/vim81/doc/Īdding 'diversion of /usr/share/vim/vim81/doc/tags to /usr/share/vim/vim81/doc/tags 216385 files and directories currently installed.) Selecting previously unselected package vim-runtime. Get:2 eoan/main amd64 vim amd64 2:-5ubuntu2 Get:1 eoan/main amd64 vim-runtime all 2:-5ubuntu2 The following NEW packages will be installed:Ġ upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 64 not upgraded.Īfter this operation, 33.4 MB of additional disk space will be used. The following additional packages will be installed: But the locate command doesn’t seem to have that. Here, we will see how to create files and add content to them using cat command.įirst of all, create a directory and named it as New_directory, execute the mkdir command as follows: How to display file details (size, date, etc.) from Linux locate command Asked 9 years, 11 months ago Modified 9 years, 11 months ago Viewed 54k times 9 The (slow) Linux find command has an option, -ls, to display size, date, etc. It is used to create a file, display the content of the file, concatenate the contents of multiple files, display the line numbers, and more. The cat command is one of the most used commands in Linux. Let's understand the above methods in detail: 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
